Alligator Facts
When you think of an alligator, it is easy for a dinosaur to come to mind.
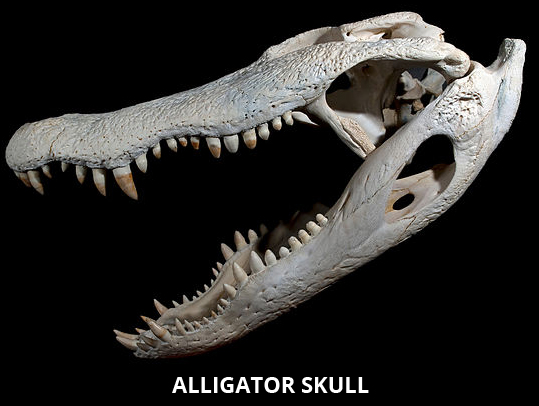
With their huge jaws, scaly skin, and sharp claws, these creatures look a lot like monsters from a scary movie instead of an animal that lives in ponds and swamps.
Keep reading to find out more facts about alligators!
Quick Alligator Facts
- Alligators are one of the few reptiles that haven’t evolved much since the dinosaur ages.
- Alligators are fast runners with the ability to run at least 35 miles per hour, but they get tired easily.
- Alligators emit the loudest sounds of any reptiles in the world.
- The blood of alligators contains both antibiotic and antiviral properties.
- A significant percentage of baby alligators get eaten by their parents.
- Even though alligators are usually carnivores, they also eat fruits.
- The average alligator goes through anywhere from 2,000 to 3,000 teeth in its lifetime.
What Are The Characteristics Of An Alligator?
Alligators belong to the reptile family, which means that they are cold-blooded, have a backbone, and are covered in dry skin with scales.
Alligators have been living on Earth for millions of years, and are sometimes called ‘living fossils’ because they have not changed very much since the times of the dinosaurs.
They are massive animals that can weigh over 800 pounds and be as long as 10 to 13 feet. This is about as long as a car!
Alligators have long, round snouts and are usually very dark green or black in color.

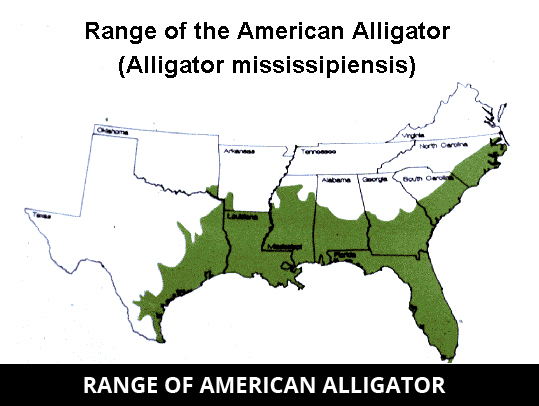
Where Do Alligators Live? What US States Have Alligators?
There are two different kinds of alligator: the American alligator and the Chinese alligator. American alligators can be found in the southeastern part of the United States, in places like Florida, Louisiana, and Georgia.
They live in freshwater environments like swamps, ponds, marshes, rivers, and lakes.
Chinese alligators can be found in the Yangtze River valley in China. They are extremely endangered, however, so they are found more often in zoos than in the wild.
Chinese alligators are much smaller than American alligators, and are usually only six feet long and weigh under 100 pounds.
What Do Alligators Like To Eat?
Alligators are a top predator in their environment and can eat almost anything they choose. When they are younger, they mainly like to eat smaller things like fish, worms, snails, and insects.
As they get bigger and stronger, they start eating bigger animals like large fish, turtles, muskrats, deer, and even other reptiles.

Alligators have even been seen ambushing big animals like panthers and black bears, making them the biggest threat to animals around the area.
While they don’t just jump out at anything they see, they can be mean and aggressive if they feel like they need to protect themselves. So it is important that you never try to go near an alligator if you see one!
Alligators can survive two to three years without eating.
How Do Alligators Hunt?
When an alligator is ready to attack its prey, there are a couple of different ways they may hunt. Thanks to their dark color and excellent camouflage, it is fairly easy for them to slowly sneak up on animals before they attack.
For smaller prey like fish or birds, alligators will eat them whole in one bite.
For larger prey, they usually grab it in their strong jaw and drag it into the water to drown it.
Then they do what is called the “death roll”. This is when alligators bring their prey on land and then wildly roll around until bite-sized chunks come off for them to chew.
Do Alligators Live Alone Or In Groups?
Large male alligators live alone and do not like to share their space with anyone or anything. They defend their territory and make sure nothing gets near them.
Smaller alligators, like young alligators and females, often live in groups near to each other. This helps them to defend their young and their territory.
Alligators Are Ancient
Alligators are ancient creatures that have roamed the Earth for millions of years. With a lineage dating back to the time of the dinosaurs, these reptiles have survived through the ages, adapting to changing environments and remaining formidable predators. Their sturdy bodies, armored scales, and powerful jaws make them well-suited for their semi-aquatic lifestyle. Despite their ancient origins, wild alligators continue to thrive in various habitats today, serving as a living link to a bygone era and a testament to the resilience of nature’s design.
They Can’t Survive In Saltwater
Alligators are well-adapted to freshwater environments but can’t survive in saltwater. Their physiology is not designed to handle the high salt concentration found in the ocean or brackish water. Unlike some other reptiles, such as crocodiles, alligators lack specialized salt glands that allow them to excrete excess salt. If exposed to saltwater for an extended period, alligators can become dehydrated and suffer from electrolyte imbalances, which can be fatal. They are primarily found in freshwater habitats like swamps, lakes, and rivers, where they thrive and exhibit their impressive survival skills.
Their Sex Is Determined By The Temperature
Alligators exhibit a fascinating phenomenon known as temperature-dependent sex determination. Unlike mammals, their sex is not determined by genetic factors but rather by the temperature at which their eggs are incubated. Cooler temperatures during incubation tend to produce male alligators, while warmer temperatures result in female alligator. This unique adaptation allows alligator populations to maintain a balance of males and females based on environmental conditions. The intricate relationship between temperature and sex determination in alligators highlights the remarkable diversity of reproductive strategies in the animal kingdom.
Their Eyes Glow In The Dark
Alligators, known for their formidable presence, possess a captivating feature: their eyes glow in the dark. Adapted to their nocturnal lifestyle, the alligator’s eyes exhibit a mesmerizing luminescence that pierces through the darkness. This intriguing phenomenon is attributed to a layer of cells called tapetum lucidum, which reflects light back through the retina, enhancing their night vision capabilities. When encountered in the depths of night, the glowing eyes of an alligator evoke a sense of primal wonder, emphasizing their mastery of the shadows and their place as true creatures of the night.
Quick Facts About Alligators:
- Alligators belong to the reptile family.
- They are cold-blooded and have dry, scaly skin.

- They have long, round snouts and are dark green or black.
- They can be 13 feet long and up to 800 pounds.
- The live in freshwater areas like ponds, marshes, rivers, and lakes.
- Alligators eat fish, turtles, muskrat, deer, and even bears.
- Alligators are strong and fierce animals that have been around for millions of years. They are top predators and rule the animals in their environment.
- As long as we protect them, and leave them alone, they will continue to rule for many years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do crocodiles ever meet alligators?
Crocodiles and alligators can potentially meet in areas where their habitats overlap, such as in certain regions of the southeastern United States. However, their encounters are relatively rare due to habitat preferences and behavior differences. When they do meet, they typically exhibit avoidance behavior and try to stay away from each other.
2. How long can alligators hold their breath?
Alligators can hold their breath for an average of 20 to 30 minutes. Their ability to remain submerged for extended periods is due to their specialized lung structure, which allows for efficient gas exchange. However, some larger individuals have been known to hold their breath for up to an hour.
3. Do alligators have night vision?
Yes, alligators have excellent night vision which is really a interesting alligator fact. They possess a specialized structure in their eyes called the tapetum lucidum, which enhances their ability to see in low-light conditions. This adaptation allows them to be effective hunters and navigate their surroundings even in darkness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alligators are fascinating creatures that have adapted and thrived in various environments for millions of years. They possess remarkable physical attributes, such as their powerful jaws and strong tails, which make them formidable predators.
Their unique nesting behaviors and parental care highlight their intelligence and social interactions. Alligators play an essential role in their ecosystems, shaping biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance.
However, they also face threats from habitat loss and human activities, emphasizing the need for conservation efforts to protect these remarkable reptiles. By understanding and appreciating alligators, we can ensure their species’ preservation and contribute to preserving our natural world.