Constitutional Amendments For Kids
A constitutional amendment is an addition or change to the Constitution of the United States.
The Constitution was signed on September 17, 1787. The first ten amendments to the Constitution, known as the Bill of Rights, were approved on December 15, 1791.
Since then, thousands of amendments to the Constitution have been suggested. Only 17 of these suggested amendments have passed. Today, there are 27 constitutional amendments in total.

How are amendments made?
The reason that most amendments don’t pass is because becoming an official amendment is a complicated process.
First, the amendment must be proposed by a two-thirds vote in Congress, including both the Senate and the House of Representatives.
An amendment can also be proposed by a national convention made up of two-thirds of the states. However, all the current constitutional amendments were proposed by Congress.
Next, the amendment must be ratified (approved). It can be ratified by three-fourths of the state legislatures or by three-fourths of the states. Every amendment except the 21st was ratified using the state legislature method.

Amendments 1-27
Of course, getting so many people to agree isn’t easy. That’s why so far, we have only 27 amendments. Let’s look at Amendments 1-27.
First Amendment

The First Amendment to the United States Constitution was adopted in 1791. This Ammendment gives right to freedom of speech, religion, and the press.
Read more about the First Amendment
Second Amendment

The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution was adopted in 1791. It gives right to the citizen to bear arms to protect themselves.
Read more about the Second Amendment
Third Amendment
The Third Amendment was adopted in 1791. This laws says that people can’t be forced to house soldiers in their homes during peacetime.
Read more about the Third Amendment
Fourth Amendment
The Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution was adopted in 1791. This law says government can’t enter private homes or search private property without a warrant and a good reason for conducting the search.
Read more about the Fourth Amendment
Fifth Amendment
The Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution was adopted in 1791. The Fifth Amendment covers several topics, including the grand jury, double jeopardy, due process of law, and self-incrimination.
Read more about the Fifth Amendment
Sixth Amendment

The Sixth Amendment to the United States Constitution was adopted in 1791.
This law says that citizens have the right to a speedy and public trial by an impartial jury. Additional rights include having a lawyer, bringing their own witnesses to trial, and more.
Read more about the Sixth Amendment
Seventh Amendment
Being the Part of first ten amendment, It was also first adopted in 1791. This law says that civil cases are non-criminal disputes between two private individuals or organizations.
Read more about the Seventh Amendment
Eighth Amendment
The Eighth Amendment was adopted in 1791. It protects people from having to pay unreasonably high fines or unreasonably high bail to be released from jail while awaiting trial.
Read more about the Eighth Amendment
Ninth Amendment
The Ninth Amendment was adopted in 1791. It explains that people’s rights are not limited only to the rights that are listed in the Constitution. People have additional rights that are not included.
Read more about the Ninth Amendment
Tenth Amendment
The Tenth Amendment was adopted in 1791. This Amendment says that the federal government only has the powers that are listed in the Constitution. Any power that is not listed in the Constitution belongs to the states and/or the people.
Read more about the Tenth Amendment
Eleventh Amendment
The Eleventh Amendment says that U.S. states can’t be sued by out-of-state citizens or by citizens of another country. It was ratified on February 7, 1795.
Read more about the Eleventh Amendment.
Twelfth Amendment
The Twelfth Amendment changed the way the President and Vice President were elected. It was ratified on June 15, 1804.
Read more about the Twelfth Amendment.

Thirteenth Amendment
The Thirteenth Amendment abolished slavery and involuntary servitude. It was ratified on December 6, 1865.
Although many slaves had already been freed under the Emancipation Proclamation, this amendment solidified their legal status as free men and women.
Read more about the Thirteenth Amendment.
Fourteenth Amendment
The Fourteenth Amendment defined United States citizenship. It also prohibits states from reducing or interfering with the rights of citizens and says that all citizens have the right to due process and the equal protection of the law.
It was ratified on July 9, 1868.
Read more about the Fourteenth Amendment.

Fifteenth Amendment
The Fifteenth Amendment gave all men the right to vote, regardless of race or color. The amendment granted the right to vote to former slaves. It was ratified on February 3, 1870.
Read more about the Fifteenth Amendment.
Sixteenth Amendment
The Sixteenth Amendment declared that the federal government has the power to collect income tax. It was ratified on February 3, 1913.
Read more about the Sixteenth Amendment.
Seventeenth Amendment
The Seventeenth Amendment established that Senators would be directly elected by popular vote. It was ratified on April 8, 1913.
Read more about the Seventeenth Amendment.

Eighteenth Amendment
The Eighteenth Amendment made alcoholic drinks illegal. It was ratified on January 16, 1919.
Read more about the Eighteenth Amendment.
Nineteenth Amendment
The Nineteenth Amendment gave women the right to vote. It was ratified on August 18, 1920.
Read more about the Nineteenth Amendment.

Twentieth Amendment
The Twentieth Amendment provided dates for the end of presidential and vice-presidential terms, as well as the terms of Senators and Representatives.
It also explained who would become president if the president-elect died. It was ratified on January 23, 1933.
Read more about the Twentieth Amendment.
Twenty-First Amendment
The Twenty-First Amendment repealed the Eighteenth Amendment. It made alcoholic drinks legal again. It was ratified on December 5, 1933.
Read more about the Twenty-First Amendment.

Twenty-Second Amendment
The Twenty-Second Amendment limited the president to a maximum of two terms. It was ratified on February 27, 1951.
Read more about the Twenty-Second Amendment.
Twenty-Third Amendment
The Twenty-Third Amendment gave Washington, D.C. representatives in the Electoral College. This allows residents of Washington D.C. to be represented in the presidential election even though they are not officially part of any state.
It was ratified on March 29, 1961.
Read more about the Twenty-Third Amendment.

Twenty-Fourth Amendment
The Twenty-Fourth Amendment declared that people did not have to pay a poll tax in order to vote. It was ratified on January 23, 1964.
Read more about the Twenty-Fourth Amendment.
Twenty-Fifth Amendment
The Twenty-Fifth Amendment established that the vice president becomes president if the president dies, resigns, or is removed from office.
It also explains who is next in line if something happens to the Vice President, and so on. It was ratified on February 10, 1967.
Read more about the Twenty-Fifth Amendment.
Twenty-Sixth Amendment
The Twenty-Sixth Amendment said that eighteen is the national voting age. It was ratified on July 1, 1971.
Read more about the Twenty-Sixth Amendment.
Twenty-Seventh Amendment
The Twenty-Seventh Amendment says that Congress cannot give themselves raises. They may vote on a raise that will take effect during the next session of Congress. It was ratified on May 7, 1992.
Read more about the Twenty-Seventh Amendment.

Other Interesting Facts About Constitutional Amendments
The Twenty-Seventh Amendment was proposed in 1792. It wasn’t ratified until 1992.
The Twenty-First Amendment is the only constitutional amendment that repeals another constitutional amendment.
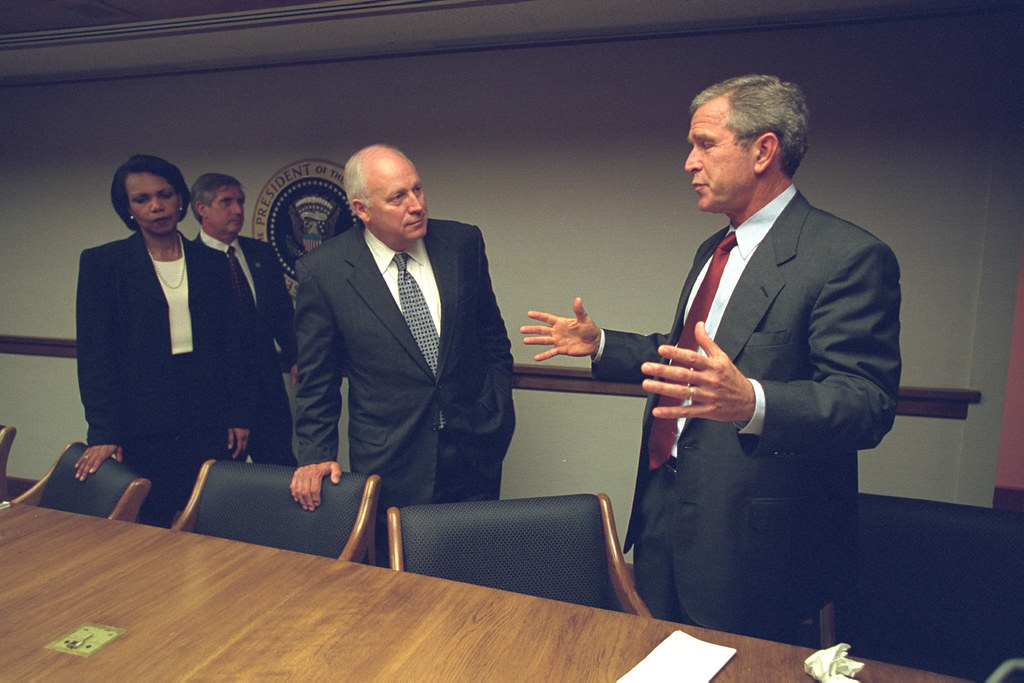
The Twenty-Fifth Amendment also allows the president to temporarily hand power to the vice president if he is unable to perform his duties (due to illness, injury, etc.). It has been used three times, once by Ronald Reagan and twice by George W. Bush.

More than 11,600 constitutional amendments have been proposed. 33 have been sent to the states for ratification. And of course, only 27 of those have been approved. No new amendments have been ratified for over 20 years.
